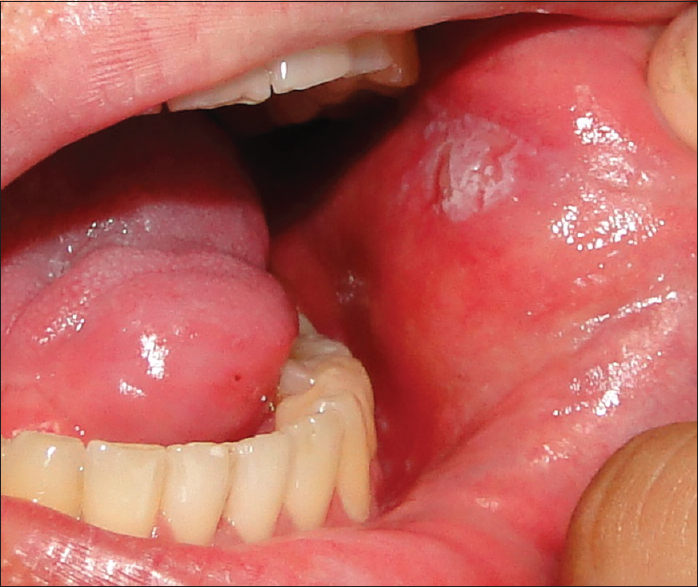
BUCCAL MUCOSA CANCER
Inner cheek cancer (also called buccal mucosa cancer) is a type of head and neck cancer that begins when the cells that make up the inner cheek grow out of control and form lesions or tumors.
Buccal mucosa SCC is known to be aggressive in nature compared with oral cancers at other sites. It has been reported to have poor local control and 5-year cause-specific survival rates in early-stage carcinomas compared with those in the oral cavity, tongue, and mouth floor
What are the causes and risk factors of buccal mucosa cancer?
- Tobacco (cigarettes or smokeless) and alcohol use greatly increases the risk of contracting buccal mucosa cancer
- More common in men
- Occurs in women who use snuff
- More likely to occur at 50 to 80 years of age but can develop at any time
What are the symptoms of buccal mucosa cancer?
There are no symptoms in the early stage. Later symptoms include:
- White or red lump in the mouth that does not go away after two weeks
- A red, raised patch in the mouth that bleeds easily
- A lump or thickening in the mouth
- Pain increases when eating or drinking
- Soreness or a feeling that something is caught in the throat
- Difficulty chewing or swallowing
- Severe ear pain
- Difficulty moving the jaw or tongue
- Hoarseness
- Numbness of the tongue or other areas of the mouth
- Dentures fit poorly or become uncomfortable because the jaw is swollen